Tag Enciclopedia Médica: Miembro inferior
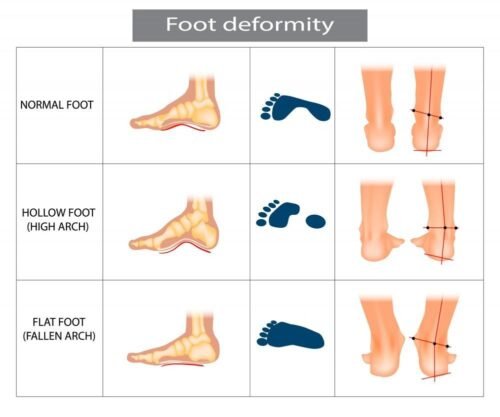
Flat feet can cause pain and affect walking
Flatfoot is a condition in which the longitudinal arch of the foot is lost. It also involves abduction of the forefoot and valgus deformity of the hind foot. In flexible flatfoot, the arch is present during non–weight bearing but is lost during weight bearing. In rigid flatfoot, the arch is absent in weight-bearing and non–weight-bearing positions.
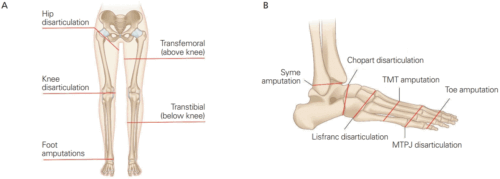
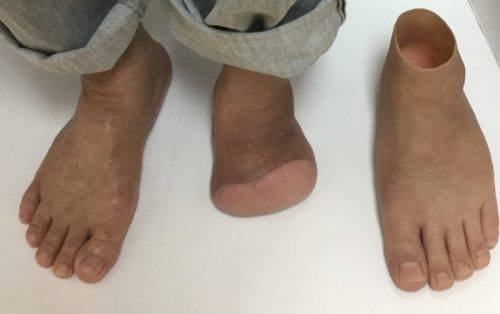
Leg or foot amputation
Leg or foot amputation is the removal of a leg, foot or toes from the body. These body parts are called extremities. Amputations are done either by surgery.

Tetra-amelia syndrome
Tetra-amelia syndrome (sometimes known as TETAMS) is a very rare disorder characterized by the absence of all four limbs.

Ectrodactyly
Ectrodactyly-Ectodermal Dysplasia-Clefting Syndrome (EEC) EEC syndrome, there are three different forms of EEC: EEC type 1, 2 and 3. Only one family has been identified with EEC 1 and 2. The most common type is EEC 3. Ectrodactyly ectodermal dysplasia cleft lip/palate (EEC) syndrome is a rare genetic disorder. Symptoms can vary greatly from one person to another. Affected individuals often have abnormalities affecting the limbs, including ectrodactyly, a condition in which part or all of the central digits (fingers or toes) are missing. Ectrodactyly often affects the middle fingers or toes, but can present differently in different people (or be absent altogether). A groove or gap in the upper lip (cleft lip) and a groove or gap in the roof

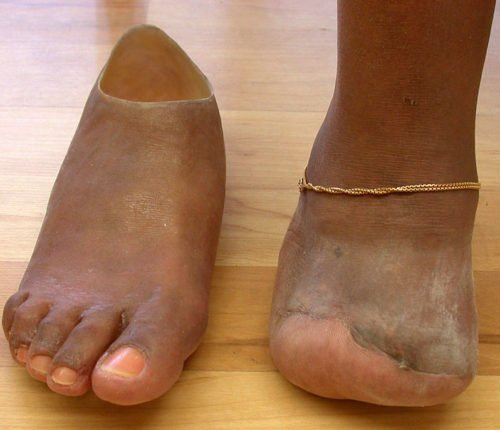
Limb difference
“Limb” is another name for the arms or legs. Limb differences are when an arm or leg is not shaped in the usual way. For example, a child’s legs may be curved or one might be shorter than the other. Or, a bone in the arm may be short or missing. A limb difference that a child is born with is called congenital. A limb difference that happens after birth is called acquired.

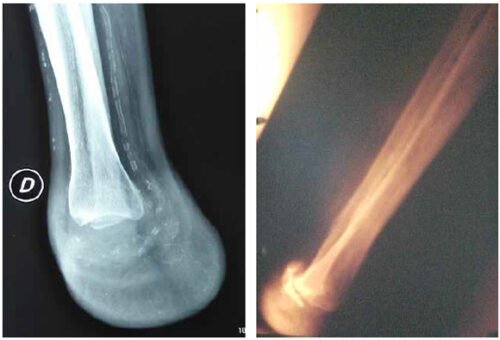
Fibular Hemimelia
There is little information on fibular hemimelia because it is so rare. It can be scary for new parents who aren’t sure what is wrong with their child, especially when their doctors haven’t seen a case of Fibular Hemimelia. Fibular Hemimelia, currently called Longitudinal Fibular Deficiency, is characterized by a completely missing or partially missing fibula bone. Each person’s leg has two bones-the tibia and fibula- and people with fibular hemimelia are missing part or all of their fibula. Due to the absence of this bone, it often results in a bowed tibia, with the affected leg being shorter than the non-affected leg.
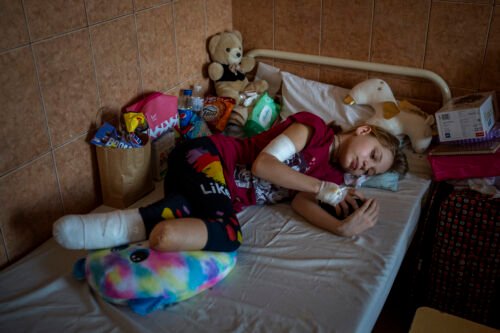
Bomb casualty amputations
Acts of terrorism tend to erode the sense of security and safety that we normally enjoy. Terrorism challenges the stability we enjoy in a predictable, orderly, and controlled world. Feelings of anger, frustration, helplessness, fear, guilt, distress, and a desire to seek revenge are all common responses.
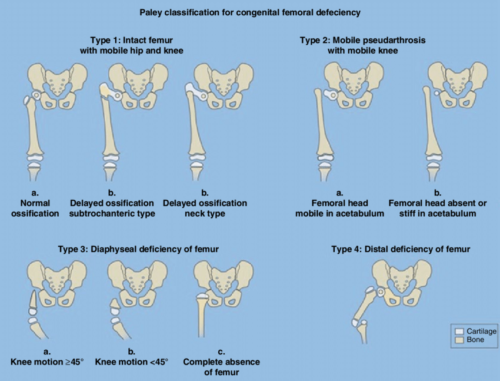
Proximal Femoral Focal Deficiency
Proximal focal femoral deficiency (PFFD) is part of a spectrum of congenital deformities affecting the femur, more comprehensively named congenital femoral.

Amputated for shark attack
According to the International Shark Attack File (ISAF), between 1958 and 2016 there were 2,785 confirmed unprovoked shark attacks around the world, of which 439 were fatal. Between 2001 and 2010, an average of 4.3 people a year died as a result of shark attacks.

Tree crush amputation
Traumatic amputation is the loss of a body part, usually a finger, toe, arm, or leg, that occurs as the result of a tree crush accident or injury.
Pie Humano * Pág.3.6. Amputación de Pirogoff
La amputación de Pirogoff fue descrita originalmente por el cirujano ruso Nicolás Pirogoff en el año 1864 y se refiere a la amputación osteoplástica distal a la articulación del tobillo, la resección del astrágalo y la fusión ósea de la tibia con el calcáneo, sus ventajas son: menor pérdida de la longitud de la extremidad y permitir la carga completa del peso corporal, así como el poder utilizar una prótesis más anatómica.
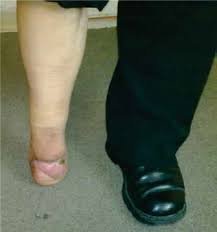
Pie Humano * Pág.3.5. Amputación de Syme o desarticulación del tobillo
Una amputación de Syme, es el nombre que recibe el proceso quirúrgico denominado desarticulación de tobillo, en otras palabras, es la operación que consiste en separar todo el pie del resto del cuerpo.
Pie Humano * Pág.3.4. Amputación de Chopart o transtarsiana
Una amputación de Chopart es la competencia más directa de la amputación de Syme. Esta amputación se realiza a través de la articulación naviculocuneiforme y cuboideometarsiana. A su favor tiene la facilidad técnica y no producir acortamiento de la extremidad.
Pie Humano * Pág.3.3. Amputación de Lisfranc o tarsometatarsiana
Una amputación de Lisfranc supone la desinserción del TA y del PB, por lo que para obtener buenos resultados es esencial rebalancear las fuerzas musculares reimplantando estos tendones. De la misma forma, es preceptivo el alargamiento del Aquiles (sobre todo en diabéticos).

Pie Humano * Pág.3.2. Amputación transmetatarsiana
La amputación transmetatarsiana (amputación parcial del pie), también llamada ATM, es la cirugía para quitar toda o una parte de su parte delantera del pie. La parte delantera de su pie incluye los huesos metatarsianos, que son cinco huesos largos entre los dedos y el tobillo.
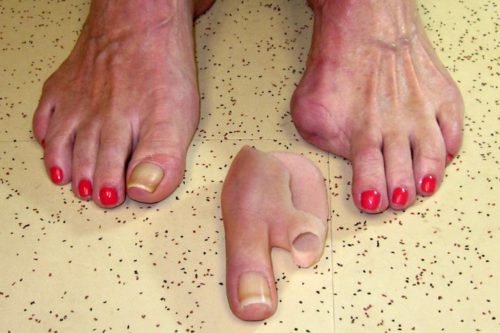
Pie Humano * Pág.3.1. Amputación de los dedos
Es la extirpación de los dedos de los pies (amputación parcial). Estas partes del cuerpo se denominan extremidades. Las amputaciones ocurren ya sea por cirugía, accidente o traumatismo. Sus causantes son diversas.
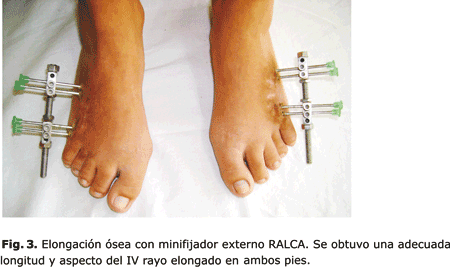
La Braquimetatarsia * Pág.3. Tratamiento mediante elongación ósea con minifijador externo
Se presentan los resultados de la elongación ósea con minifijador externo, en una serie de 6 pacientes afectados de braquimetatarsia. Los pacientes fueron tratados en el Complejo Científico Ortopédico Internacional “Frank País” durante los años 2003 al 2007 (ambos inclusive).
En 5 pacientes la afección fue bilateral por lo cual se trataron un total de 11 pies.
En todos los casos la anomalía se localizó en el IV metatarsiano. Todos los pacientes pertenecen al sexo femenino y la edad promedio en el momento de la cirugía fue de 13,2 años. El alargamiento promedio logrado fue de 16 mm (12-21). El tiempo promedio de consolidación fue de 2,2 meses por cm de hueso elongado. En tres pies se presentaron complicaciones: retardo de consolidación, infección superficial en el trayecto de los alambres y contractura en flexión a nivel de la articulación metatarsofalángica del dedo correspondiente.

