Tag Enciclopedia Médica: Manos
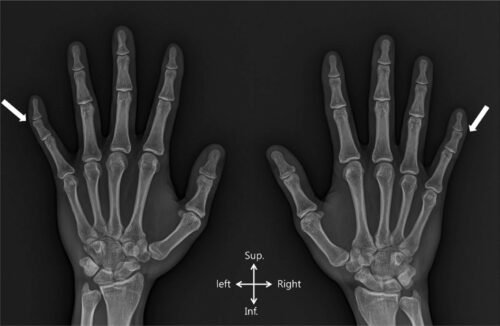
Clinodactyly
Clinodactyly is a medical term describing the curvature of a digit (a finger or toe) in the plane of the palm, most commonly the fifth finger (the “little finger”) towards the adjacent fourth finger (the “ring finger”).

Ectrodactyly
Ectrodactyly-Ectodermal Dysplasia-Clefting Syndrome (EEC) EEC syndrome, there are three different forms of EEC: EEC type 1, 2 and 3. Only one family has been identified with EEC 1 and 2. The most common type is EEC 3. Ectrodactyly ectodermal dysplasia cleft lip/palate (EEC) syndrome is a rare genetic disorder. Symptoms can vary greatly from one person to another. Affected individuals often have abnormalities affecting the limbs, including ectrodactyly, a condition in which part or all of the central digits (fingers or toes) are missing. Ectrodactyly often affects the middle fingers or toes, but can present differently in different people (or be absent altogether). A groove or gap in the upper lip (cleft lip) and a groove or gap in the roof

Tree crush amputation
Traumatic amputation is the loss of a body part, usually a finger, toe, arm, or leg, that occurs as the result of a tree crush accident or injury.
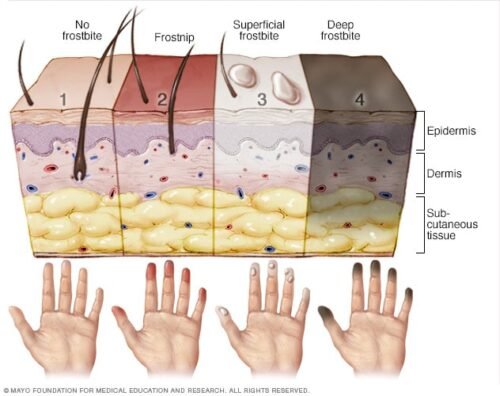
Frostbite amputations
Areas that are usually affected include cheeks, ears, nose, and fingers and toes. Frostbite is often preceded by frostnip. The symptoms of frostbite progress with prolonged exposure to cold. Historically, frostbite has been classified by degrees according to skin and sensation changes, similar to burn classifications. However, the degrees do not correspond to the amount of long term damage. A simplification of this system of classification is superficial (first or second degree) or deep injury (third or fourth degree).
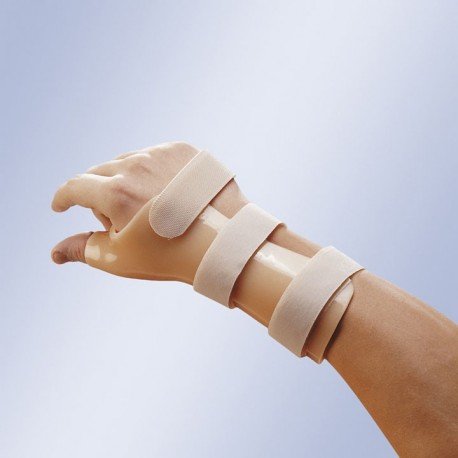
Ortesis convencionales Pág.2. Miembro superior
Las ortesis son dispositivos, soportes y apoyos elaborados con la finalidad de brindar asistencia al sistema neuromusculoesquelético, los cuales realizan trabajos de sujeción, estabilización, alineación o corrección. Se clasifican de acuerdo a la parte del cuerpo donde son utilizadas, siendo las siguientes las más importantes:
– Ortesis para miembros superiores.
– Ortesis para miembros inferiores.
– Ortesis para columna vertebral
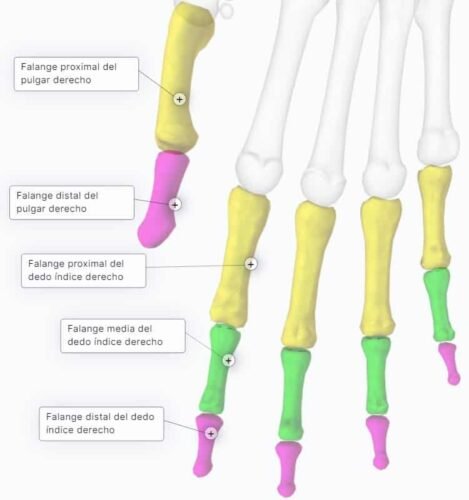
Mano humana * Pág.4. Las falanges
El primer dedo (dedo gordo) presenta, solo dos falanges, mientras que los otros cuatro dedos presentan tres: falange proximal, medial y distal.
Cada falange tiene una base, un cuerpo y una cabeza. (En posición anatómica el dedo gordo se encuentra lateralmente al contrario que en el pie).
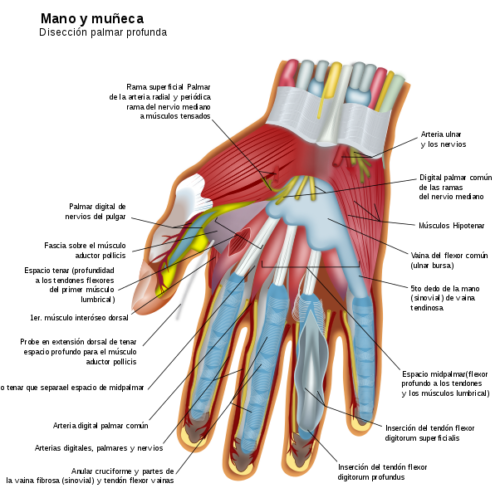
Mano humana * Pág.3. Partes
Las manos contienen más huesos y partes móviles que la mayoría de las otras zonas del cuerpo. Cuando están sanas, todas estas partes funcionan en colaboración para efectuar una gran cantidad de tareas diferentes, desde movimientos muy delicados hasta acciones que requieren mucha fuerza.
Nivel de la amputación * Pág.2. Miembro superior
El nivel de amputación es la altura a la cual se secciona una parte del cuerpo. Los niveles de amputación en la protésica de miembro superior son:

Mano humana * Pág.5. Amputaciones
Es la ausencia, perdida o mutilación de toda o parte de la mano humana.
Las amputaciones de las manos tienen diversos orígenes, siendo los más comunes las causas traumáticas, congénitas o como consecuencia de enfermedades.
