Multipágina Biblioteca: Amputación Traumática * Páginas

Limb difference
“Limb” is another name for the arms or legs. Limb differences are when an arm or leg is not shaped in the usual way. For example, a child’s legs may be curved or one might be shorter than the other. Or, a bone in the arm may be short or missing. A limb difference that a child is born with is called congenital. A limb difference that happens after birth is called acquired.

Horse accident leads for amputation
Head injuries are the most common reason for admission to hospital or death among riders. Sobering statistics reveal the high percentage of equine-related accidents resulting in traumatic brain injury, and helmets have been associated with reducing the risk of traumatic brain injury by as much as 50 percent. Yet, many riders still do not wear a helmet.

Paralympic athletes
A Paralympian is an athlete who competes in the Paralympic games. They’re athletes that have bodily differences and different types of disabilities.
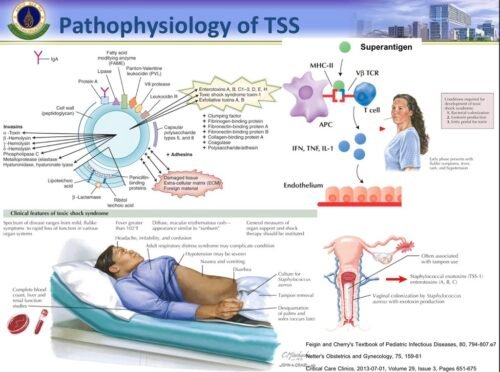
Toxic shock syndrome TSS
Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is a condition caused by bacterial toxins. Symptoms may include fever, rash, skin peeling, and low blood pressure. There may also be symptoms related to the specific underlying infection such as mastitis, osteomyelitis, necrotising fasciitis, or pneumonia. A few possible causes of toxic shock syndrome are: Cuts or open wounds on the skin, Surgical wounds, Viral infections (e.g. chickenpox), Contraceptive sponges, History of a recent birth, miscarriage, or abortion, Using super-absorbent tampons, Previously having TSS
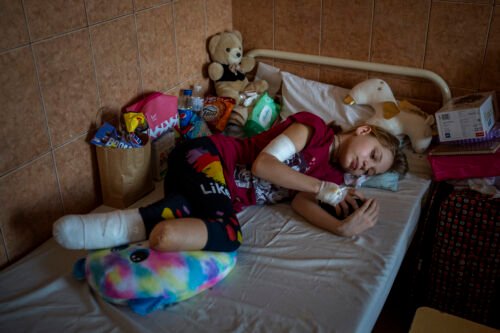
Bomb casualty amputations
Acts of terrorism tend to erode the sense of security and safety that we normally enjoy. Terrorism challenges the stability we enjoy in a predictable, orderly, and controlled world. Feelings of anger, frustration, helplessness, fear, guilt, distress, and a desire to seek revenge are all common responses.

Amputation accidents
Losing a limb is one of the most traumatic physical injuries that a person can experience. In addition to being a devastating physical injury, amputation injuries can also have a significant impact on a person’s mental health. Depending on the nature of the injury and the body part that was amputated, an injured victim may require multiple surgeries and months of physical rehabilitation, including getting fitted for and learning how to use a prosthetic, and occupational therapy.

Amputated for shark attack
According to the International Shark Attack File (ISAF), between 1958 and 2016 there were 2,785 confirmed unprovoked shark attacks around the world, of which 439 were fatal. Between 2001 and 2010, an average of 4.3 people a year died as a result of shark attacks.

Tree crush amputation
Traumatic amputation is the loss of a body part, usually a finger, toe, arm, or leg, that occurs as the result of a tree crush accident or injury.
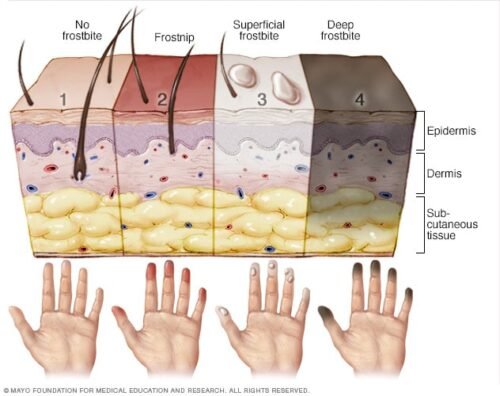
Frostbite amputations
Areas that are usually affected include cheeks, ears, nose, and fingers and toes. Frostbite is often preceded by frostnip. The symptoms of frostbite progress with prolonged exposure to cold. Historically, frostbite has been classified by degrees according to skin and sensation changes, similar to burn classifications. However, the degrees do not correspond to the amount of long term damage. A simplification of this system of classification is superficial (first or second degree) or deep injury (third or fourth degree).

Amputation for electric shock
Serious, disabling and disfiguring injuries are common and can happen after an electric shock injury. These injuries may include: (1) heart damage; (2) brain damage; (3) burns; (4) nerve damage; and/or (5) miscarriage.

Amputation for train crash
Train accidents have been known to cause serious injuries. This can include serious head injuries. These types of injuries including permanent disfigurement, serious burns and amputations often require life-long care. Victims and their families are often left with little compensation for their injuries.

Amputations caused by car accidents
A traffic collision, also known as a motor vehicle collision or car crash, is when a vehicle hits another vehicle, person, or object. Pedestrians, animals, road debris or other objects may be involved. Sometimes a trial occurs, in order to determine fault in a traffic collision.
Amputación traumática. Pág.2. Cirugía radical en el aparato locomotor
La amputación es irreversible; ningún miembro artificial posee percepción sensitiva, de manera que es importante no eliminar una extremidad que tenga intacta su sensibilidad (aunque con dolor tolerable), aun cuando haya desaparecido la función motora.
La mayor parte de las técnicas de amputación en los adultos son útiles también para niños, pero, en estos casos, los factores de crecimiento corporal general y de crecimiento del muñón son bastante significativos.
Por ejemplo, una amputación en la mitad del muslo en un niño de cinco años, puede dar por resultado un muñón extremadamente corto a la edad de catorce años, porque se eliminó la epífisis femoral inferior; en contraste, una amputación por debajo de la rodilla en la que se preserva un muñón muy corto a los cinco años, puede determinar un muñón satisfactorio a los catorce años, porque habrá continuado el crecimiento de la epífisis tibial superior
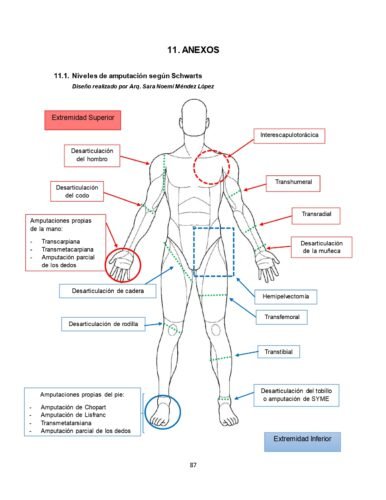
Amputación Traumática. Pág.1. Todo al respecto
La amputación traumática completa se define como la separación total de un segmento del miembro del resto del cuerpo. En la amputación incompleta o parcial queda algo de tejido blando de conexión, pero hay sección completa de los vasos principales y, al menos, del 75 % de las partes blandas. Las causas de una amputación son múltiples, que derivan en la amputación completa o parcial de una extremidad, entre las causas se encuentran: diabetes, cáncer, trastornos vasculares, infecciones, malformaciones congénitas y trauma.


