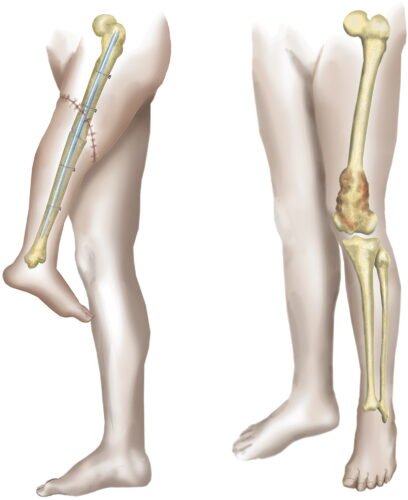
Rotationplasty, commonly known as a Van Nes rotation or Borggreve rotation, is a type of autograft wherein a portion of a limb is removed, while the remaining limb below the involved portion is rotated and reattached. This procedure is used when a portion of an extremity is injured or involved with a disease, such as cancer.
The bottom of the femur, the knee, and the upper tibia are surgically removed. The lower leg is then rotated 180 degrees (which is why it’s called rotationplasty) and then attached to the femur.
The procedure is most commonly used to transfer the ankle joint to the knee joint following removal of a distal femoral bone tumor, such as osteosarcoma. The limb is rotated because the ankle flexes in the opposite direction compared to the knee. The benefit to the patient is that they have a functioning knee joint to which a prosthetic can be fitted, so that they can run and jump.