Categoría Enciclopedia Médica: Enfermedades
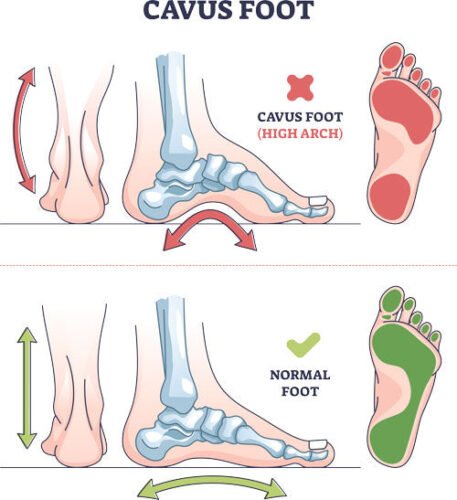
High arch is the opposite of flat feet
High arch: High arches are a genetically inherited condition where your arch is much higher or raised than normal. When weight-bearing, there is significantly more space in between the floor and the arch.
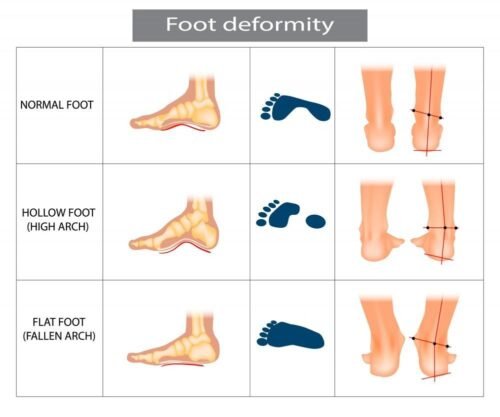
Flat feet can cause pain and affect walking
Flatfoot is a condition in which the longitudinal arch of the foot is lost. It also involves abduction of the forefoot and valgus deformity of the hind foot. In flexible flatfoot, the arch is present during non–weight bearing but is lost during weight bearing. In rigid flatfoot, the arch is absent in weight-bearing and non–weight-bearing positions.
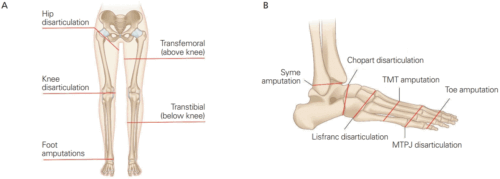
Leg or foot amputation
Leg or foot amputation is the removal of a leg, foot or toes from the body. These body parts are called extremities. Amputations are done either by surgery.
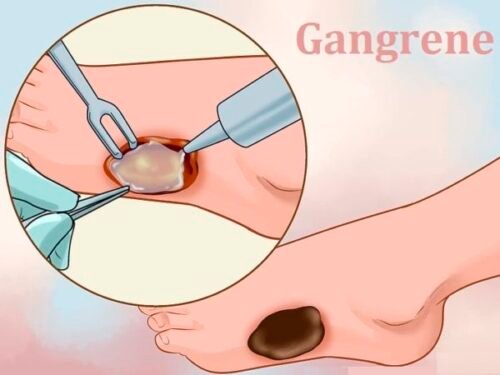
Gangrene
Gangrene happens when tissues in your body die after a loss of blood caused by illness, injury, or infection. It usually happens in extremities like fingers, toes, and limbs, but you can also get gangrene in your organs and muscles. There are different types of gangrene, and all of them need medical care right away.

Physical disability
A physical disability is a substantial and long-term limitation affecting a person’s mobility, physical functioning, stamina or agility. It can limit the individual, either temporarily or permanently, by becoming disabled for a wide range of reasons, such as genetic disorder, injury or a specific condition.
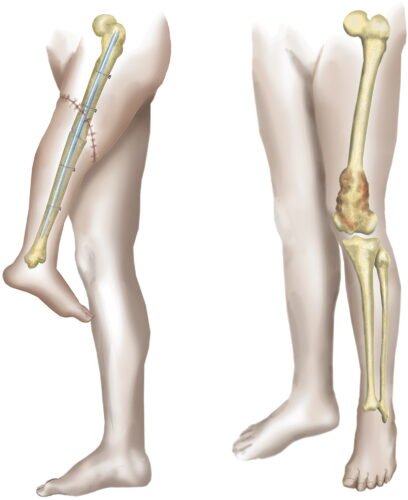
Rotationplasty or Van Nes rotation
Rotationplasty, commonly known as a Van Nes rotation or Borggreve rotation, is a type of autograft wherein a portion of a limb is removed, while the remaining limb below the involved portion is rotated and reattached.
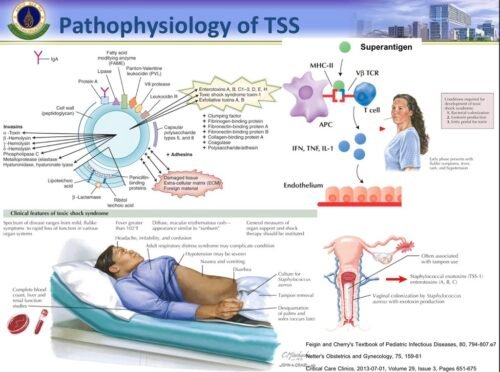
Toxic shock syndrome TSS
Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is a condition caused by bacterial toxins. Symptoms may include fever, rash, skin peeling, and low blood pressure. There may also be symptoms related to the specific underlying infection such as mastitis, osteomyelitis, necrotising fasciitis, or pneumonia. A few possible causes of toxic shock syndrome are: Cuts or open wounds on the skin, Surgical wounds, Viral infections (e.g. chickenpox), Contraceptive sponges, History of a recent birth, miscarriage, or abortion, Using super-absorbent tampons, Previously having TSS
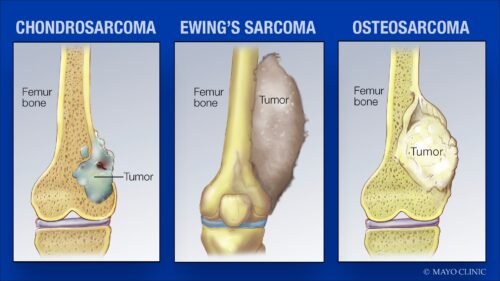
Amputation for bone cancer
Bone cancer can be one of several different cancers that develop in the bones. Cancers that begin in the bone are called primary bone cancers. Tumours that begin in organs or other parts of the body can also spread to the bones. Treatments include surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Amputation for bacterial infection in blood
Blood infections, also known as sepsis, can be fatal if not treated immediately. This is why it’s crucial to know the warning signs of sepsis and how to stop it in its tracks. Blood infections occur when your body is experiencing a severe reaction to an illness. People 65 or younger than 1 are more at risk for sepsis than others. If you can spot the warning signs of a blood infection quickly, it can potentially save your life.
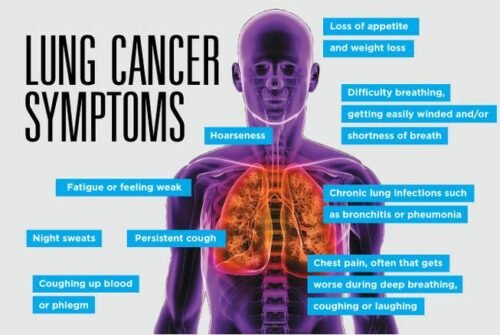
Lung cancer
Lung cancer with bone metastases refers to secondary or metastatic tumours that are formed from cancer cells that have broken away from a primary lung cancer and spread through the lymphatic system or blood stream to the bones. Lung cancer is the third most common cause of bone metastases.
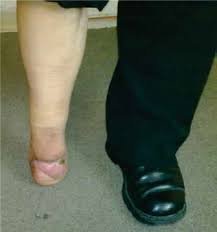
Pie Humano * Pág.3.6. Amputación de Pirogoff
La amputación de Pirogoff fue descrita originalmente por el cirujano ruso Nicolás Pirogoff en el año 1864 y se refiere a la amputación osteoplástica distal a la articulación del tobillo, la resección del astrágalo y la fusión ósea de la tibia con el calcáneo, sus ventajas son: menor pérdida de la longitud de la extremidad y permitir la carga completa del peso corporal, así como el poder utilizar una prótesis más anatómica.
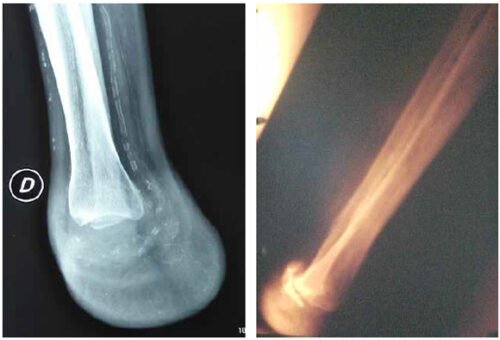
Pie Humano * Pág.3.5. Amputación de Syme o desarticulación del tobillo
Una amputación de Syme, es el nombre que recibe el proceso quirúrgico denominado desarticulación de tobillo, en otras palabras, es la operación que consiste en separar todo el pie del resto del cuerpo.
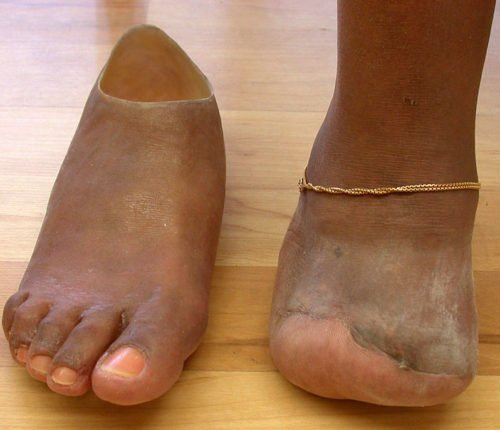
Pie Humano * Pág.3.4. Amputación de Chopart o transtarsiana
Una amputación de Chopart es la competencia más directa de la amputación de Syme. Esta amputación se realiza a través de la articulación naviculocuneiforme y cuboideometarsiana. A su favor tiene la facilidad técnica y no producir acortamiento de la extremidad.
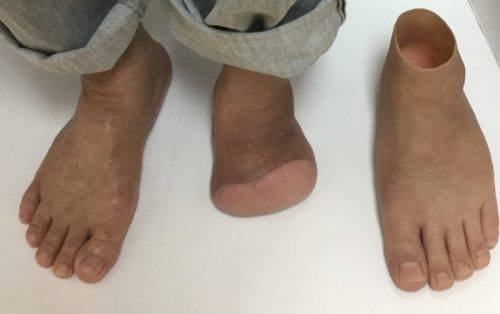
Pie Humano * Pág.3.3. Amputación de Lisfranc o tarsometatarsiana
Una amputación de Lisfranc supone la desinserción del TA y del PB, por lo que para obtener buenos resultados es esencial rebalancear las fuerzas musculares reimplantando estos tendones. De la misma forma, es preceptivo el alargamiento del Aquiles (sobre todo en diabéticos).

Pie Humano * Pág.3.2. Amputación transmetatarsiana
La amputación transmetatarsiana (amputación parcial del pie), también llamada ATM, es la cirugía para quitar toda o una parte de su parte delantera del pie. La parte delantera de su pie incluye los huesos metatarsianos, que son cinco huesos largos entre los dedos y el tobillo.
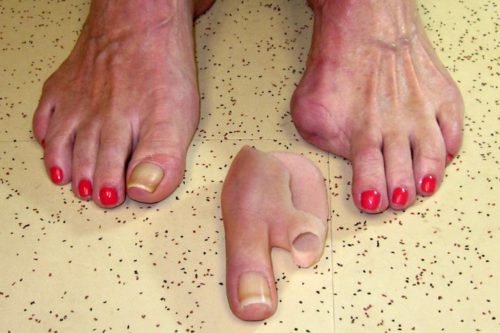
Pie Humano * Pág.3.1. Amputación de los dedos
Es la extirpación de los dedos de los pies (amputación parcial). Estas partes del cuerpo se denominan extremidades. Las amputaciones ocurren ya sea por cirugía, accidente o traumatismo. Sus causantes son diversas.
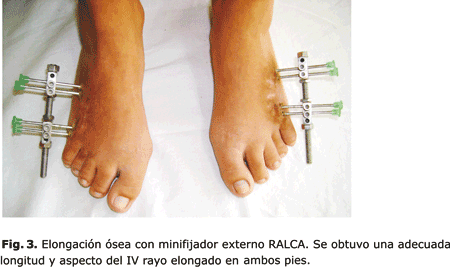
La Braquimetatarsia * Pág.3. Tratamiento mediante elongación ósea con minifijador externo
Se presentan los resultados de la elongación ósea con minifijador externo, en una serie de 6 pacientes afectados de braquimetatarsia. Los pacientes fueron tratados en el Complejo Científico Ortopédico Internacional “Frank País” durante los años 2003 al 2007 (ambos inclusive).
En 5 pacientes la afección fue bilateral por lo cual se trataron un total de 11 pies.
En todos los casos la anomalía se localizó en el IV metatarsiano. Todos los pacientes pertenecen al sexo femenino y la edad promedio en el momento de la cirugía fue de 13,2 años. El alargamiento promedio logrado fue de 16 mm (12-21). El tiempo promedio de consolidación fue de 2,2 meses por cm de hueso elongado. En tres pies se presentaron complicaciones: retardo de consolidación, infección superficial en el trayecto de los alambres y contractura en flexión a nivel de la articulación metatarsofalángica del dedo correspondiente.

