Categoría Enciclopedia Médica: Anatomía
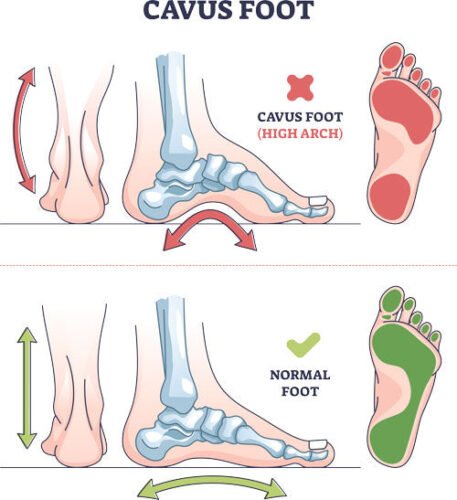
High arch is the opposite of flat feet
High arch: High arches are a genetically inherited condition where your arch is much higher or raised than normal. When weight-bearing, there is significantly more space in between the floor and the arch.
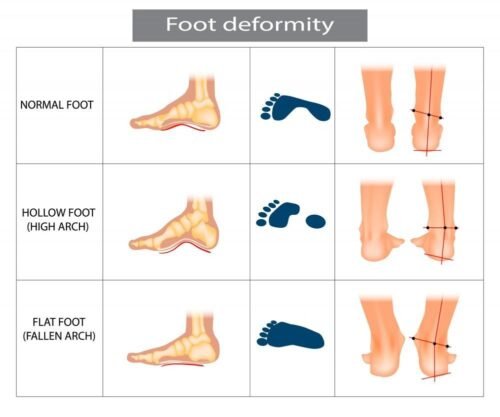
Flat feet can cause pain and affect walking
Flatfoot is a condition in which the longitudinal arch of the foot is lost. It also involves abduction of the forefoot and valgus deformity of the hind foot. In flexible flatfoot, the arch is present during non–weight bearing but is lost during weight bearing. In rigid flatfoot, the arch is absent in weight-bearing and non–weight-bearing positions.
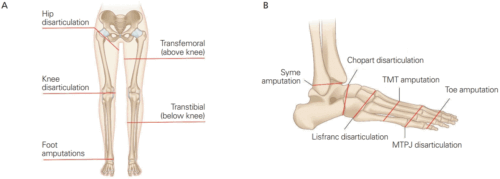
Leg or foot amputation
Leg or foot amputation is the removal of a leg, foot or toes from the body. These body parts are called extremities. Amputations are done either by surgery.
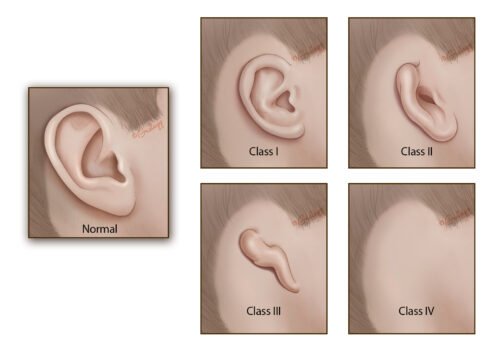
Microtia
Microtia and Atresia are congenital birth defects of the ear. Microtia is when the outer ear does not fully develop during the first trimester of pregnancy or when the outer ear is absent, (known as anotia). Atresia is the absence of the ear canal, resulting in hearing loss. Microtia and Atresia occurs in every 1 out of 6,000 to 12,000 births.
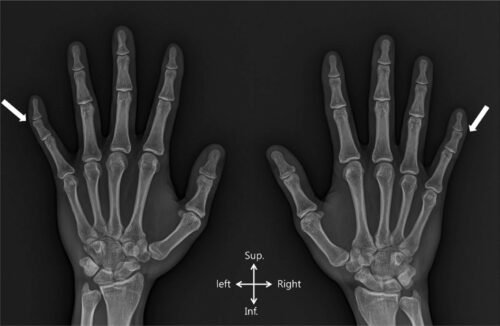
Clinodactyly
Clinodactyly is a medical term describing the curvature of a digit (a finger or toe) in the plane of the palm, most commonly the fifth finger (the “little finger”) towards the adjacent fourth finger (the “ring finger”).

Ectrodactyly
Ectrodactyly-Ectodermal Dysplasia-Clefting Syndrome (EEC) EEC syndrome, there are three different forms of EEC: EEC type 1, 2 and 3. Only one family has been identified with EEC 1 and 2. The most common type is EEC 3. Ectrodactyly ectodermal dysplasia cleft lip/palate (EEC) syndrome is a rare genetic disorder. Symptoms can vary greatly from one person to another. Affected individuals often have abnormalities affecting the limbs, including ectrodactyly, a condition in which part or all of the central digits (fingers or toes) are missing. Ectrodactyly often affects the middle fingers or toes, but can present differently in different people (or be absent altogether). A groove or gap in the upper lip (cleft lip) and a groove or gap in the roof

Limb difference
“Limb” is another name for the arms or legs. Limb differences are when an arm or leg is not shaped in the usual way. For example, a child’s legs may be curved or one might be shorter than the other. Or, a bone in the arm may be short or missing. A limb difference that a child is born with is called congenital. A limb difference that happens after birth is called acquired.

Fibular Hemimelia
There is little information on fibular hemimelia because it is so rare. It can be scary for new parents who aren’t sure what is wrong with their child, especially when their doctors haven’t seen a case of Fibular Hemimelia. Fibular Hemimelia, currently called Longitudinal Fibular Deficiency, is characterized by a completely missing or partially missing fibula bone. Each person’s leg has two bones-the tibia and fibula- and people with fibular hemimelia are missing part or all of their fibula. Due to the absence of this bone, it often results in a bowed tibia, with the affected leg being shorter than the non-affected leg.

Paralympic athletes
A Paralympian is an athlete who competes in the Paralympic games. They’re athletes that have bodily differences and different types of disabilities.
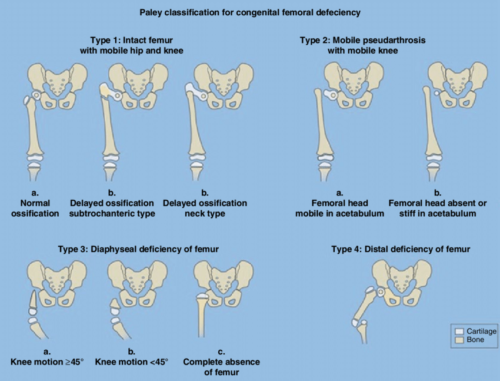
Proximal Femoral Focal Deficiency
Proximal focal femoral deficiency (PFFD) is part of a spectrum of congenital deformities affecting the femur, more comprehensively named congenital femoral.

Congenital amputation
A congenital amputation means a limb is not formed correctly or is missing at birth. This happens while the limb is being formed in the womb. It is often: • Not genetic, meaning passed from parent to child • Not because of anything you did or did not do before your baby was born Congenital amputations may include one or more of the following: • Different limb lengths • Poor joint function • Weak muscles • Fragile skin.

Tree crush amputation
Traumatic amputation is the loss of a body part, usually a finger, toe, arm, or leg, that occurs as the result of a tree crush accident or injury.

Piel humana * Pag.3.2 Trastornos más comunes
Los trastornos de la piel varían mucho en cuanto a síntomas y gravedad. Pueden ser temporales o permanentes, y podrían ser indoloros o causar dolor

Piel humana * Pag.3.1 Trastornos más comunes
Los trastornos de la piel varían mucho en cuanto a síntomas y gravedad. Pueden ser temporales o permanentes, y podrían ser indoloros o causar dolor
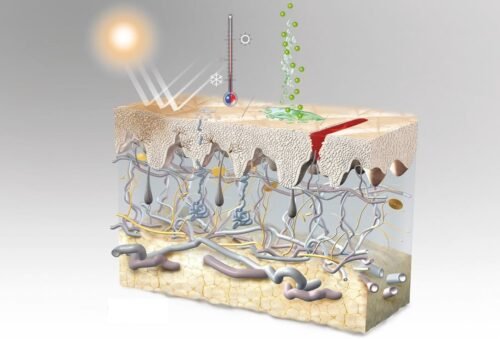
Piel humana * Pag.2. Fisiología
Las funciones principales de la piel son 1) Ser barrera protectora, 2) Regular el metabolismo y la temperatura y 3) Sintetizar la Vitamina D
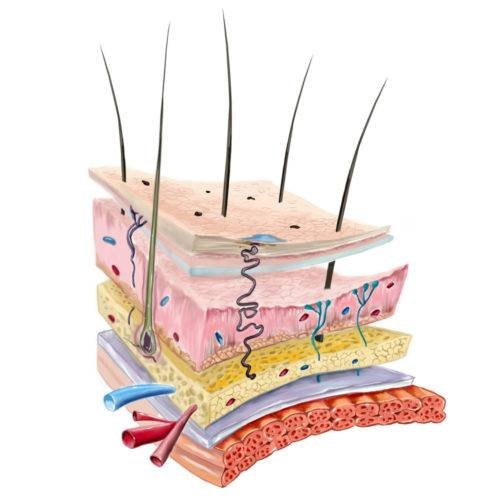
Piel humana * Pag.1. Anatomía
La piel es la frontera del organismo con el medio externo. Su función primordial es la adaptación y la conexión del individuo con el medio ambiente
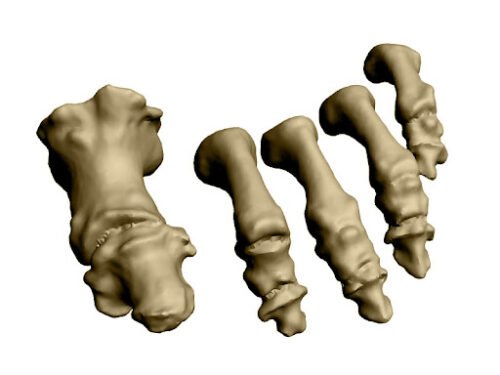
Pie Humano * Pág.1.2. Falanges
El primer dedo (dedo gordo) presenta, solo dos falanges, mientras que los otros cuatro dedos presentan tres: falange proximal, medial y distal.
Cada falange tiene una base, un cuerpo y una cabeza. (En posición anatómica el dedo gordo se encuentra lateralmente al contrario que en el pie).

